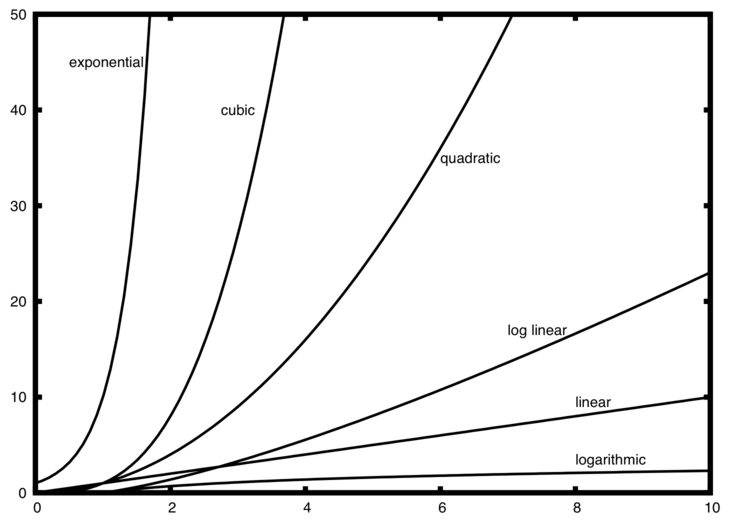
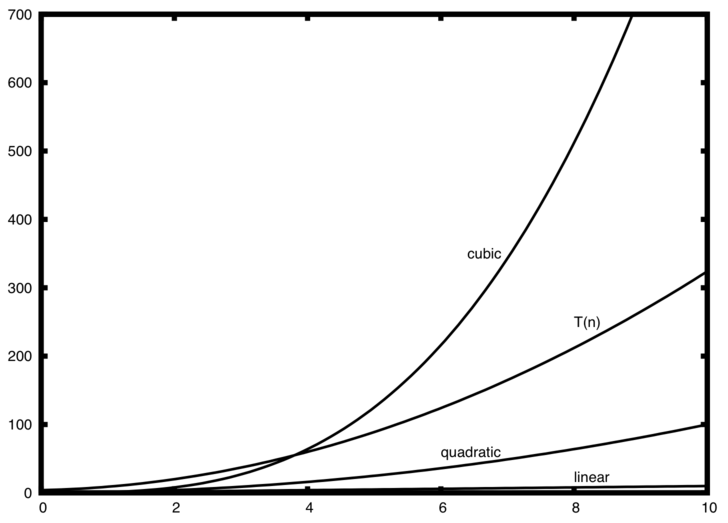
Big(o) notation Order:
 |
List in Data Structure:
A linked list is a sequence of data structures, which are connected together via links. Linked List is a sequence of links which contains items. Each link contains a connection to another link. Linked list is the second most-used data structure after array.
Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Linked List.
Link − Each link of a linked list can store a data called an element.
Next − Each link of a linked list contains a link to the next link called Next.
LinkedList − A Linked List contains the connection link to the first link called First.
Linked List Representation
Linked list can be visualized as a chain of nodes, where every node points to the next node.

As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
Linked List contains a link element called first.
Each link carries a data field(s) and a link field called next.
Each link is linked with its next link using its next link.
Last link carries a link as null to mark the end of the list.
Types of Linked List
Following are the various types of linked list.
Simple Linked List − Item navigation is forward only.
Doubly Linked List − Items can be navigated forward and backward.
Circular Linked List − Last item contains link of the first element as next and the first element has a link to the last element as previous.
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by a list.
Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
Display − Displays the complete list.
Search − Searches an element using the given key.
Delete − Deletes an element using the given key.
Insertion Operation
Adding a new node in linked list is a more than one step activity. We shall learn this with diagrams here. First, create a node using the same structure and find the location where it has to be inserted.

Imagine that we are inserting a node B (NewNode), between A (LeftNode) and C (RightNode). Then point B.next to C −
NewNode.next −> RightNode;
It should look like this −

Now, the next node at the left should point to the new node.
LeftNode.next −> NewNode;

This will put the new node in the middle of the two. The new list should look like this −

Similar steps should be taken if the node is being inserted at the beginning of the list. While inserting it at the end, the second last node of the list should point to the new node and the new node will point to NULL.
Deletion Operation
Deletion is also a more than one step process. We shall learn with pictorial representation. First, locate the target node to be removed, by using searching algorithms.

The left (previous) node of the target node now should point to the next node of the target node −
LeftNode.next −> TargetNode.next;

This will remove the link that was pointing to the target node. Now, using the following code, we will remove what the target node is pointing at.
TargetNode.next −> NULL;

We need to use the deleted node. We can keep that in memory otherwise we can simply deallocate memory and wipe off the target node completely.

Reverse Operation
This operation is a thorough one. We need to make the last node to be pointed by the head node and reverse the whole linked list.

First, we traverse to the end of the list. It should be pointing to NULL. Now, we shall make it point to its previous node −

We have to make sure that the last node is not the last node. So we'll have some temp node, which looks like the head node pointing to the last node. Now, we shall make all left side nodes point to their previous nodes one by one.

Except the node (first node) pointed by the head node, all nodes should point to their predecessor, making them their new successor. The first node will point to NULL.

We'll make the head node point to the new first node by using the temp node.

Data Structure - Doubly Linked List
Doubly Linked List is a variation of Linked list in which navigation is possible in both ways, either forward and backward easily as compared to Single Linked List. Following are the important terms to understand the concept of doubly linked list.
Link − Each link of a linked list can store a data called an element.
Next − Each link of a linked list contains a link to the next link called Next.
Prev − Each link of a linked list contains a link to the previous link called Prev.
LinkedList − A Linked List contains the connection link to the first link called First and to the last link called Last.
Doubly Linked List Representation

As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
Doubly Linked List contains a link element called first and last.
Each link carries a data field(s) and two link fields called next and prev.
Each link is linked with its next link using its next link.
Each link is linked with its previous link using its previous link.
The last link carries a link as null to mark the end of the list.
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by a list.
Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
Insert Last − Adds an element at the end of the list.
Delete Last − Deletes an element from the end of the list.
Insert After − Adds an element after an item of the list.
Delete − Deletes an element from the list using the key.
Display forward − Displays the complete list in a forward manner.
Display backward − Displays the complete list in a backward manner.
Data Structure - Circular Linked List
Circular Linked List is a variation of Linked list in which the first element points to the last element and the last element points to the first element. Both Singly Linked List and Doubly Linked List can be made into a circular linked list.
Singly Linked List as Circular
In singly linked list, the next pointer of the last node points to the first node.

Doubly Linked List as Circular
In doubly linked list, the next pointer of the last node points to the first node and the previous pointer of the first node points to the last node making the circular in both directions.

As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
The last link's next points to the first link of the list in both cases of singly as well as doubly linked list.
The first link's previous points to the last of the list in case of doubly linked list.
Basic Operations
Following are the important operations supported by a circular list.
insert − Inserts an element at the start of the list.
delete − Deletes an element from the start of the list.
display − Displays the list.
Insertion Operation
Following code demonstrates the insertion operation in a circular linked list based on single linked list.
Data Structures and Algorithms - Arrays
Array is a container which can hold a fix number of items and these items should be of the same type. Most of the data structures make use of arrays to implement their algorithms. Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Array.
Element − Each item stored in an array is called an element.
Index − Each location of an element in an array has a numerical index, which is used to identify the element.
Array Representation
Arrays can be declared in various ways in different languages. For illustration, let's take C array declaration.

Arrays can be declared in various ways in different languages. For illustration, let's take C array declaration.

As per the above illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
Index starts with 0.
Array length is 10 which means it can store 10 elements.
Each element can be accessed via its index. For example, we can fetch an element at index 6 as 9.
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by an array.
Traverse − print all the array elements one by one.
Insertion − Adds an element at the given index.
Deletion − Deletes an element at the given index.
Search − Searches an element using the given index or by the value.
Update − Updates an element at the given index.
Linked list in Data structure python in hindi
Mysirg.com
Link:- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x_vX8gRdO9o
Stack in Python:-
A stack is a linear data structure that stores items in a Last-In/First-Out (LIFO) or First-In/Last-Out (FILO) manner. In stack, a new element is added at one end and an element is removed from that end only. The insert and delete operations are often called push and pop.
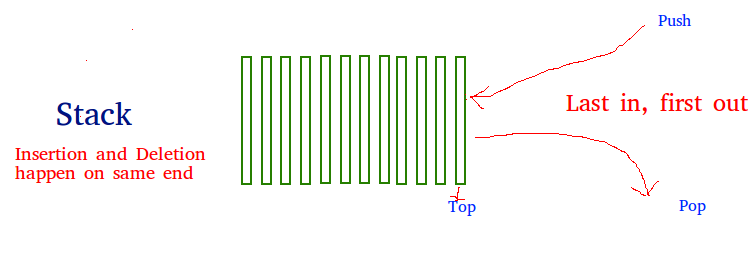
The functions associated with stack are:
- empty() – Returns whether the stack is empty – Time Complexity : O(1)
- size() – Returns the size of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
- top() – Returns a reference to the top most element of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
- push(g) – Adds the element ‘g’ at the top of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
- pop() – Deletes the top most element of the stack – Time Complexity : O(1)
Implementation
There are various ways from which a stack can be implemented in Python. This article covers the implementation of stack using data structures and modules from Python library.
Blog Link:- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-in-python/
Youtube Link :- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gxLIPj4gKKE
Queue in Python:-
Like stack, queue is a linear data structure that stores items in First In First Out (FIFO) manner. With a queue the least recently added item is removed first. A good example of queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first.
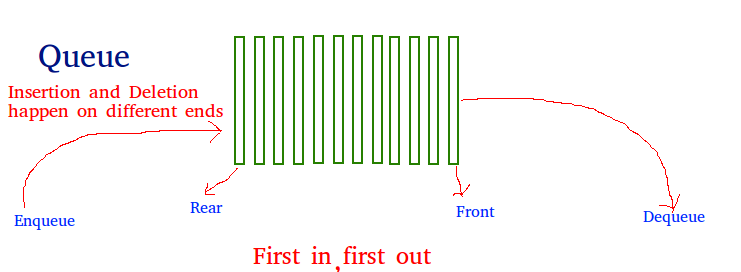
Operations associated with queue are:
- Enqueue: Adds an item to the queue. If the queue is full, then it is said to be an Overflow condition – Time Complexity : O(1)
- Dequeue: Removes an item from the queue. The items are popped in the same order in which they are pushed. If the queue is empty, then it is said to be an Underflow condition – Time Complexity : O(1)
- Front: Get the front item from queue – Time Complexity : O(1)
- Rear: Get the last item from queue – Time Complexity : O(1)
Implementation
There are various ways to implement a queue in Python. This article covers the implementation of queue using data structures and modules from Python library.
Blog link:-https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/queue-in-python/






Ak no.
ReplyDelete